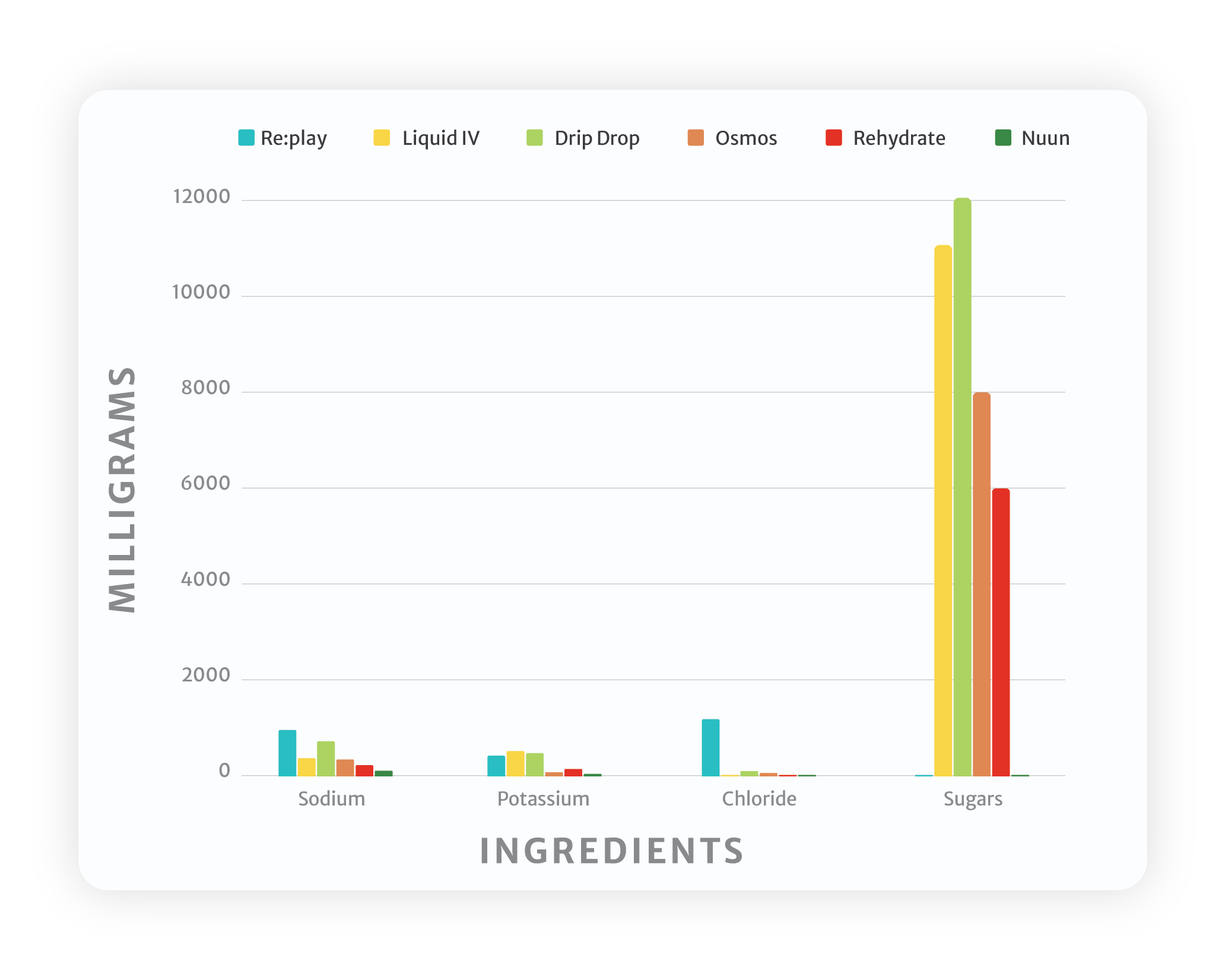
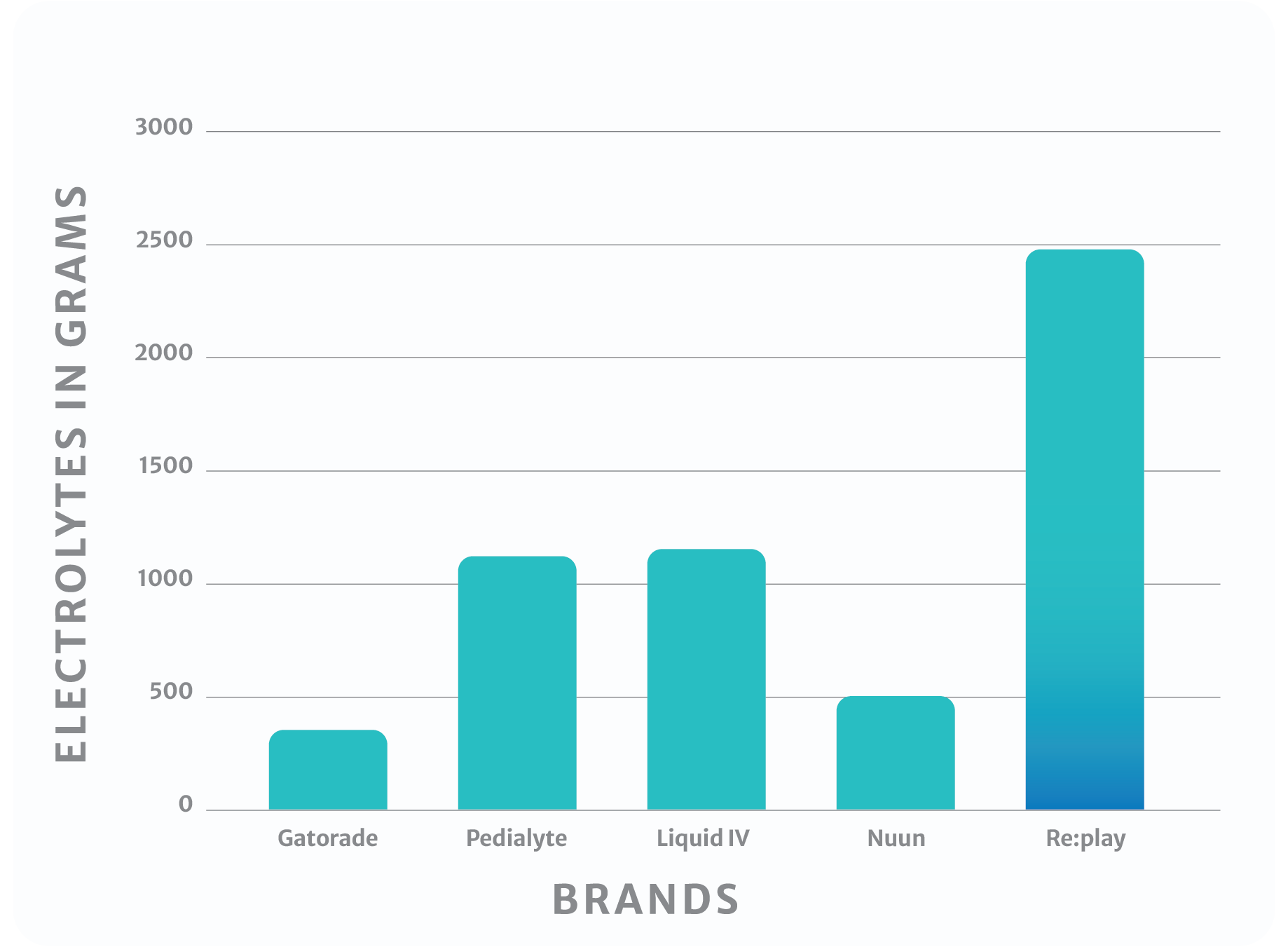
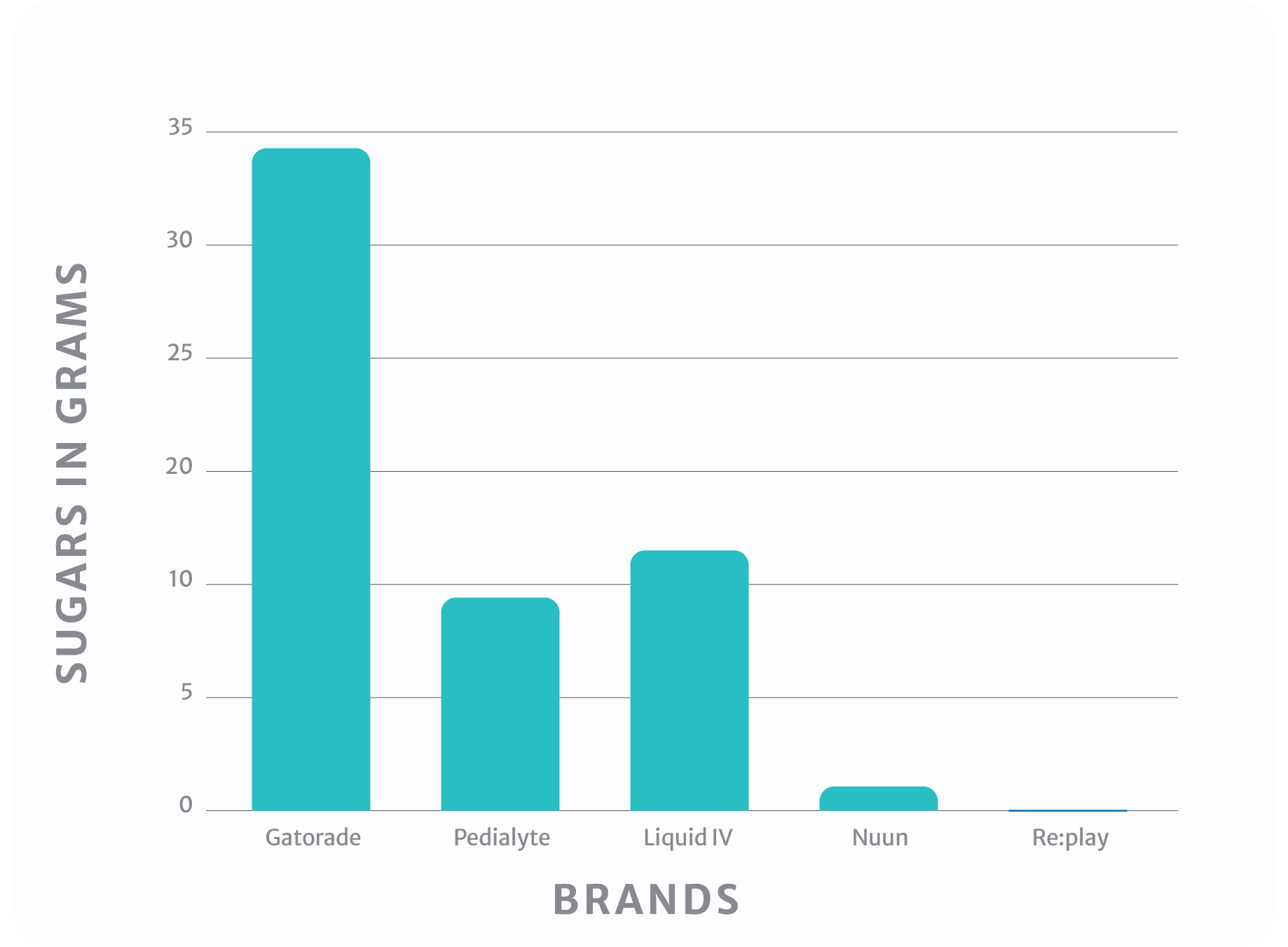
The ingredients don't lie
Hydration Science
Hydration health affects both physical and cognitive functions and is especially important when it comes to safety.
Hydrated
- Regulated body temperature
- Carries oxygen and nutrients to cells
- Protects organs and tissues
- Removes waste
- Improved physical and cognitive function
- Lubricated joints
- Increased productivity
- Increased energy levels

Dehydrated
- Slows metabolism—resulting in weight gain
- Daytime fatigue, sleepiness
- Little or no urine; urine that is darker than usual
- Dry mouth; extreme thirst
- Headaches
- Confusion
- Feeling dizzy or light-headed
- Increased risk of infections
- Impaired healing
- Decreased respiratory and cardiac function